Converting IV to SC Insulin (Not for DKA/HONK pts)
AACE guidelines. Patients w/o hx of insulin-requiring DM who are receiving <2 units/hour of IV insulin may not require transition to SC insulin. For these pts, consider starting "low dose" correction insulin scale, and use basal insulin if BG is uncontrolled.
Insulin Drip Approach
-
Determine the average hourly rate of IV insulin over last 6 hours and multiply rate x20 hrs = daily insulin requirement.
e.g., 2U/hr x 20hrs = ~40U daily IV insulin
-
Convert IV insulin to SC insulin: 50% as basal, 50% as short acting in 3 divided doses given at meals (use latter only if eating)
e.g., 40 units x 50% = 20 units;
20 units basal insulin (Glargine) once daily
20 / 3 = ~6 units short acting insulin (Aspart) TID with meals. If not eating well, can order 50% of this dose and give after patient has eaten >50% of meal. Order Aspart Insulin correction scale
Discontinue IV insulin 2 hours after 1st dose of SC insulin
Weight Based Approach
Alternatively, can start weight based insulin initiation. TODO: add protocol.
Special situations
NPO
Hold all oral agents and mealtime insulin.
-
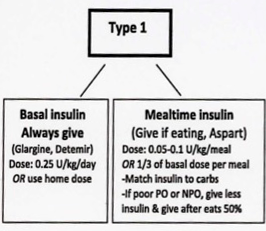
Type 1 DM:
- Minor procedure/imaging study: give 80% of basal insulin dose.
- Major surgery: insulin drip and D5 1/2NS.
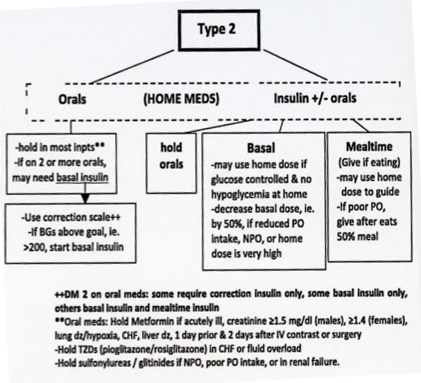
Type 2 DM: give 50-80% of basal insulin dose, if NPO >24h give only 50% of basal insulin dose.
May require D5 1/2NS, and correction insulin scale every 6 hours.
Feeds
If on continuous enteral feeds and hyperglycemic → use NPH Q&H (hold dose if tube feeds are held; if insulin given and feeds are stopped, then run D5 or D10 to avoid hypoglycemia).
Steroids
- Exacerbate postprandial > fasting BG.
May start on a correction scale to determine daily insulin needs.
If BG above goal, can use NPH with prednisone and give at the same time.
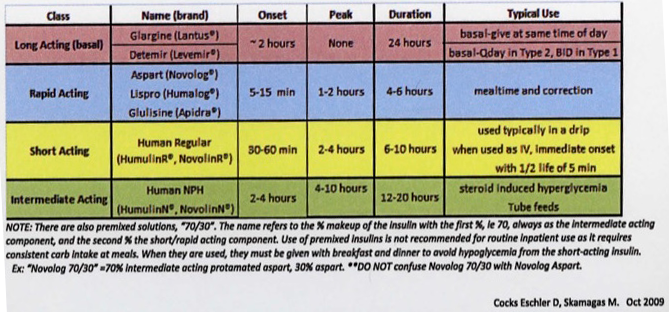
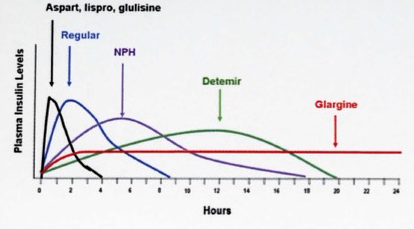
Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Insulin Subtypes (given SC)
Hypoglycemia Management for Inpatients
-
Choose from the following:
FS 50-70 and able to take PO: 4oz fruit juice
FS <50 or unable to take PO or altered mental status, give 1/2 to 1 amp of D50%
FS <50 and no IV access, give glucagon 1mg IM
Check FS in 15 minutes, repeat the above step until FS >100
Patients at increased risk for hypos: missed meals, elderly, renal/hepatic failure, pancreatic disease
Discharging home
If A1C at goal, continue pre-hospital regimen.
If A1C not at goal, consider changing regimen, and inform patient and pt's MD of change.
Prescriptions: Insulin – pens & pen needles, vials & syringes; glucometer supplies – lancets, glucometer strips, alcohol pads
Glucose goals (ADA): fasting: 70-130 mg/dL, postprandial: <180 mg/dL
Glucose monitoring: once daily if on oral meds or basal insulin; 3-4 times daily if on multiple injections/day
Hyperglycemia Management for Inpatients
Type 1 DM
Type 2 DM
Initiating Insulin - Type 2 DM
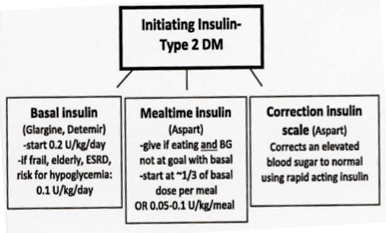
Titrating Insulin
Basal Insulin: fasting BG guides titration of basal; titrate up or down by ~10-20%/day
Mealtime Insulin: premeal BG guides titrate of bolus insulin from prior meal; titrate up or down by 1-2U per meal or 10-20% if on high dose insulin
Inpatient hyperglycemia goals
From the ADA/AACE consensus, 2009
| Location | BG Goals (mg/dL |
|---|---|
| Wards | <140 pre-meal, <180 at other times |
| ICU | 140-180; start IV insulin if BG>180 |
Order a Diabetes diet: Carbohydrate-controlled, caloric requirements: 25-30 kcal/kg/d, ~1800-2000 kcal/day
Order Hemoglobin A1C if not available from the last 3 mos.